Important information on Long COVID in the professional context
Useful information for employers and employees
How can employers deal with Long COVID?
The symptoms after a Corona virus SARS-CoV-2 infection can be extremely varied. Employees with Long COVID symptoms often no longer have the same capacity to work as before. It can happen, for example, that the long haulers can bear lesser workload due to tiredness and exhaustion. Not only this, but problems in concentration and memory, breathlessness, vascular symptoms and aches can also make the work routine difficult. It is therefore important that employers support their employees as much as possible if needed. Thus, work absences can be kept as low as possible.
In some cases, Long COVID is recognised as occupational disease or accident at work. Then the statutory accident insurance is relevant. The information portal for employers for social insurance and the information page of the Central Association of the Trade associations and Accident Insurance Companies, the Statutory Accident Insurance (DGUV), explains when a recognition can be given and what are the obligations of the employer then.
If employees are restricted by long-term effects after a Corona virus infection and want to come back to the workplace, employers can support them in various ways. It often first comes down to taking the symptoms seriously. Employers should realize that Long COVID can have extremely different progression. Therefore, every employee needs individual solutions. Hence, it makes sense that employers and long haulers stay in touch during the illness. Apart from that, it is helpful to inform the employees about there being a company doctor, as the case may be, options for reintegration or rehab offers. The flyer of the German Pension Insurance gives an overview of rehab programmes specifically for reintegration in professional life. In addition, Bundesarbeitsgemeinschaft für Rehabilitation e. V. [National Association for Rehabilitation] (BAR) has created a guideline with assistances for employers for introducing a reintegration management. During the rehabilitation, employees also have a claim to continued remuneration or benefits in lieu of income. Information on this is also provided in the profile of the information portal on social insurance for employees.
Employers can take various steps to support their employees in reintegration in work. A more detailed overview of this can be found in Guidelines for managements of the European Agency for Security and Health Safety at Workplace. Other helpful instructions for employers can be found in Information portal on social insurance for employers.
In some cases, employers are also responsible to undertake a so-called occupational integration management (BEM) If employees are absent longer than 6 weeks within 12 months, for example, due to Long COVID, a BEM can be helpful. A BEM shall support employees in occupational reintegration. It shall also help in preventing the recurrence of incapacity to work. Participation for employees is voluntary. The statutory basis is laid down in the Sozialgesetzbuch (SGB) [Code of Social Law] (§ 167 para. 2 of SGB IX).
Employers should pay the necessary attention to BEM and consider it as a chance. This way, the long-term effects of the COVID-19 pandemic can be kept as low as possible for the employers. Taking the offer of a BEM discussion is recommended for the affected employees. They can take the support of employee representatives, for example, the works council or staff council, as well as the company doctor. Meanwhile, the law also stipulates that employees can consult a person whom they trust for the procedure related to BEM. For severely disable employees, the representative body for the severely disabled and integration office are also consulted as a part of a BEM.
Options of how work can be taken up again are discussed together with the employee. A particular focus is on with which benefits or aids can employers support the long haulers in their comeback to work. The discussion also involves how a recurrence of incapacity to work can be prevented. The employer and employee should continue the dialogue even after the employee takes up work. The discussion can clarify, for example, whether further adjustments are necessary.
The symptoms in Long COVID turn out to vary widely. Therefore, common solutions conforming to the personal needs of the long haulers must be found out. These solutions can look extremely different on a case by case basis. Here are some examples of how employers can support long haulers:
- Adjustment of work tasks
- Change in area of work
- Adjustment of work load
- Support by team member
- Adjustment of working hours
- Flexible working hours
- Changed break times
- Adjustment of shift work
- Design of workplace
- Enabling work from home
- Provision of aids
- Adaptation of workplace
- Step by step reintegration
- Creation of a reintegration plan
Sources:
https://www.dguv.de/post-covid/index.jsp
https://www.informationsportal.de/wp-content/uploads/Steckbrief-Rehabilitation.pdf
https://osha.europa.eu/de/publications/covid-19-infection-and-long-covid-guide-workers
https://www.bgf-koordinierungsstelle.de/
Last update: July 2024
What can long haulers do in school, training, or in college studies in case of Long COVID?
What can long haulers do in school, training, or in college studies in case of Long COVID?
The regulations are different in the school or vocational school depending on the state. So, it is the best to obtain information on-site. The facility is even likely to have some measures to deal with Long COVID. Long haulers and their relatives should try to deal with their symptoms or the symptoms of their sick child as openly as possible to get the right support.
Students can find information on dealing with Long COVID on the website of the Studierendenwerk [Student Affairs]. Students and their relatives can learn there, what should be done if the student is not able to appear for an exam or study due to an illness.
In some cases of Long COVID, it can also make sense to apply for a compensation for incapacity early on. This aims at supporting pupils, college students, or trainees with a disability or chronic constrains by means of appropriate assistance. You can directly ask at the respective educational institution as to how exactly should such a request be made. In most of the cases, the health impairment and its consequences have to be proven by evidence, for example, by a medical certificate. College students can also obtain information about consulting services for a compensation for incapacity directly using the search function of the Studierendenwerk.
For children, who are looked after in day-care facilities, pupils, as well as college students also: If you were infected by the Corona virus in a care facility or in the school, this can be an insured event of statutory accident insurance. The accident insurance companies are the right contact partner in these cases.
Last update: July 2024
How many absences from work will there be in the future due to Long COVID?
We cannot say at present, how much of the working population will be affected by Long COVID in the future. Health insurance companies and accident insurance agencies have already analysed how many of their insured persons are absent from their workplace due to Long COVID in 2020. However, researchers speculate that the estimated number of unreported long haulers is far higher. It follows that an accurate prognosis of the future absences from work due to Long COVID is not yet possible. The prognosis also depends on how the Corona virus SARS-CoV-2 develops further. Apart from that, the prognosis shall be influenced by the future treatment options of COVID-19 and Long COVID.
Recently, the Techniker Krankenkasse published figures of the working population insured with them: Close to one percent of those, who had been infected by the Corona virus in 2020, were still on a sick leave in 2022 due to Long COVID. In the previous year, 2021, the Techniker Krankenkasse recorded 4,144 so-called “Post COVID-19 statuses”. The long haulers were mostly absent for long: The average number was 105 days.
An analysis of the Wissenschaftlichen Institut der AOK (WIdO) from the year 2022 reported similar figures: Since the beginning of the pandemic, more than every 5th employed, insured person has already been absent once due to a COVID-19 illness. Close to 4 per cent of the patients eventually became unfit for work due to Long COVID or Post COVID. That equals around one per cent of all the working population insured with AOK.
The applications for occupational diseases have greatly risen due to the COVID-19 illnesses according to the National Association of Statutory Accident Insurance: Around 80,000 reported suspicions of an occupational disease were received in 2019. In 2022, a total of 370,141 reports of suspicion of an occupational disease were received; an occupational disease was recognised in 199,542 cases. The main cause for the rise in reports and recognitions of occupations diseases is the corona pandemic. Around 180,000 recognitions were attributed to COVID-19 in 2022.
“Long COVID or Post COVID” was recorded in 2 per cent of the cases among the COVID-19 illnesses that were recognised as occupational disease in 2020 to 2022.
It is still unclear how the figures of the working population afflicted with Long COVID shall develop in the future. The prognosis depends on various factors: These include the knowledge from long-term studies on the course of Long COVID and the further spread of Corona virus in the population. Apart from that, the prognosis is influenced by how Long COVID shall be determined and the cases recorded in the future.
Last update: July 2024
Are there appropriate rehab offers for Long COVID?
What is a rehab?
A rehabilitation aims to improve functional limitations resulting from an illness. This can also be beneficial in the case of long-term consequences following an infection with the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. In most cases, “Reha” refers to medical rehabilitation. Medical rehabilitation consists of various treatment programmes designed to improve the state of health during or after an illness. Such rehabilitation can include, for example, medical treatment, physiotherapy or psychotherapy.
It is advisable to consider medical rehabilitation for Long COVID, especially when the symptoms, while not requiring hospitalization, do not show further improvement despite outpatient treatment.
What rehab programmes are available at Long COVID?
With Long COVID, there is no “single” rehab. The options depend on the complaints and can therefore vary greatly.
In a medical rehabilitation, physical and mental symptoms following an infection can be specifically addressed. There are various prerequisites for services for medical rehab to be approved.
There are various prerequisites for services for medical rehabilitation to be approved.
On the one hand, an improvement in symptoms through rehabilitation is expected. On the other hand, patients must have sufficient endurance to actively participate in rehabilitation. Being able to independently perform activities such as personal hygiene, eating, walking, and participating in group therapies is essential. Many rehabilitation facilities have developed specialised programs tailored to the individual needs of those affected by Long COVID. Certain treatments, for example, focus on respiratory issues or nervous system impairments, while others prioritise psychological counseling.
In addition to medical rehabilitation, there is also professional and social rehabilitation. These include assistance and benefits for participation in professional and everyday life, for example support when returning to work or the provision of aids for everyday life.
The performance, workability, and health of those affected can be sustainably impaired by the symptoms. If Long COVID sufferers are affected in their daily work by these symptoms, targeted treatment concepts are therefore needed.
In recent years, specific programs have been developed and implemented to assess and address occupational limitations. These programs are also referred to as Medical-Vocational Rehabilitation (MBOR). Such a form of rehabilitation aims to assist individuals in coping with occupational challenges. This is crucial as the symptoms of Long COVID can also impact employability. Its effectiveness has been demonstrated in various studies.
Where does rehabilitation take place?
Rehabilitation can be conducted on an outpatient basis, where the rehabilitation facility is only visited during the day. In contrast, during inpatient rehabilitation, individuals are accommodated in a rehabilitation clinic. The choice of facility is based on where the symptoms can be best treated. For example, if respiratory issues are prominent, a rehabilitation facility specializing in respiratory diseases may be appropriate. Conversely, if concentration disorders are predominant, a neurological rehabilitation facility may be advisable.
How long does rehabilitation take?
The duration of treatment depends on the type of rehabilitation. In most cases, inpatient rehab lasts around 3 weeks and outpatient rehab lasts a maximum of 20 treatment days. For children it is 4 to 6 weeks on average. An extension can be applied for with appropriate medical justification.
How do you find a rehab centre?
The application for rehabilitation with Long COVID is usually submitted by the affected person themselves. The family doctor can provide advice and support with a medical report.
The Deutsche Rentenversicherung Insurance provides an overview of various offerings in a brochure. Additionally, through the Rehabilitation Facilities Search of the Federal Working Group for Rehabilitation (BAR), one can search for facilities. For individuals for whom COVID-19 has been recognised as an occupational disease or work-related accident by statutory accident insurance, the BG Clinics offer a nationwide, structured, and interdisciplinary program. This Post COVID Programme is offered in all 12 locations of BG clinics. The statutory accident insurance has published a video for rehabilitation. The statutory pension insurance and accident insurance have formulated medical and organisational standards for the rehabilitation of Post COVID patients in a joint set of directives.
It includes consultations, outpatient clinics, a specific diagnostic clarification process, as well as inpatient rehabilitation measures and outpatient follow-up care. All rehabilitation measures are individually tailored to the needs of those affected and are supervised by various specialised disciplines.
What is follow-up rehabilitation?
If you have been seriously ill with COVID-19 and have been treated in hospital, rehabilitation is often organised while you are still in hospital. In most cases, rehabilitation follows directly after hospitalisation. This type of rehabilitation is also called “follow-up rehabilitation”. If you have any questions, the medical team on the ward or the hospital's social services are good contact points.
What is rehabilitation aftercare?
After rehabilitation, there is the option of “rehabilitation aftercare”. The aim is to consolidate the success of rehabilitation and maintain it in the long term. These options also depend on the complaints. Part of the rehabilitation aftercare can be, for example, training, personal counselling or physical training. Online options are also available for rehabilitation aftercare. Rehabilitation aftercare must be recommended by the treating physicians during rehabilitation. You should therefore discuss whether such an option is possible during your rehab programme. If it is an accident at work or an occupational disease, you should contact the rehabilitation manager of your accident insurance provider.
Important: The treatments in a rehabilitation centre should be adapted to your personal resilience. In people with stress intolerance, for example, symptoms can worsen even after slight stress. Suitable rehab is therefore very important. Affected persons can seek advice from their doctor. Affected persons can express their wishes, for example in which facility the rehabilitation should take place. These wishes are taken into account where possible.
Also see FAQ: “Can I apply for medical rehabilitation in case of Long COVID?”.
Last update: July 2024
Can I apply for a medical rehab for Long COVID?
It is possible to apply for a medical rehab for Long COVID. The family doctor can support in application. Of the long haulers are severely ill from COVID-19 and treated in the hospital, a so-called follow-up rehabilitation is mostly already organised there. In this case, the long haulers have to do nothing. The medical treatment team at the ward or the social service of the hospital can answer all questions on follow-up rehabilitation.
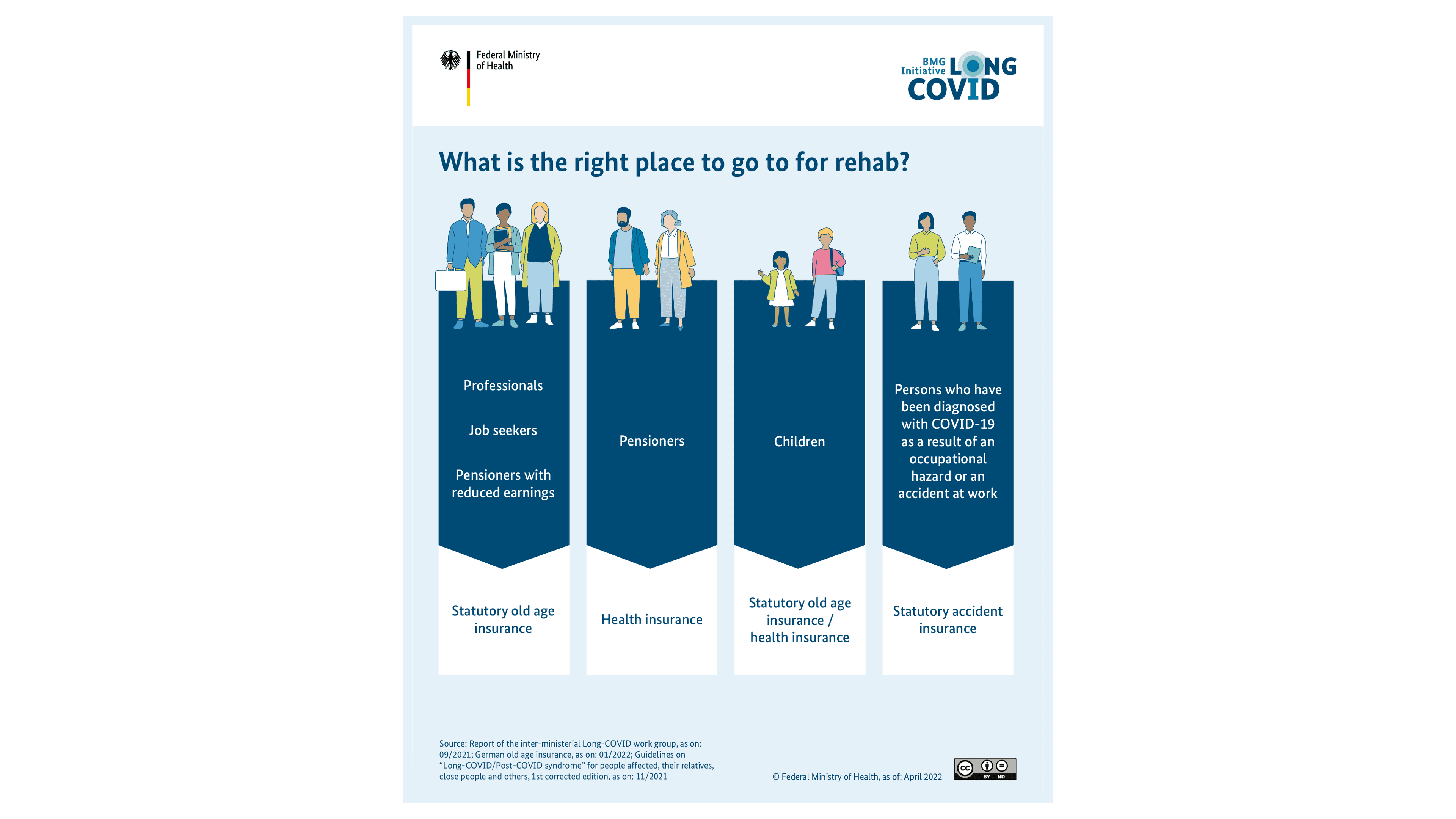
- If the long haulers were not treated in the hospital, they generally have to apply for a rehab on their own. Various cost bearers are responsible depending on the personal life situation:
- The statutory pension insurance is the cost bearer for persons insured under pension insurance according to §§ 10 et. seq. of SGB VI.
- The health insurance company bears the costs for pensioners.
- The statutory pension insurance or the health insurance company takes over the costs for children.
The statutory accident insurance takes over the costs if COVID-19 was recognised as an occupational disease or accident at work. In this case also, the long haulers do not have to apply for rehab. Instead, the accident insurance agency shall decide whether a rehab is necessary. However, the long haulers can speak to the agency about the possibility of a rehab if necessary.
If COVID-19 is not recognised as an occupational disease or accident at work, there are various contact points and cost bearers to consider. Which cost bearer is responsible depends, among other things, on the life situation.

If you are unsure, which cost bearer is responsible, the rehab responsibility navigator of the National Association for Rehabilitation (BAR) can help further. The German Pension Insurance, National Association for Rehabilitation (BAR) and National Association of Statutory Health Insurance (GKV) have also compiled further information related to rehab applications.
Depending on how the symptoms develop, a rehab follow-up can be helpful. Such a follow-up should lastingly strengthen the success of rehab treatment. Apart from that, it shall support the comeback to work life and long-term preservation of the earning capacity. A rehab follow-up can be in the form of seminars, consultation offers, or trainings. These are also offered online to some extent. Patients should already inquire already during the rehab whether a rehab follow-up is necessary or can be helpful. The attending doctor can help you further here.
Last update: July 2024
Can Long COVID be an occupations disease or an accident at work?
When can Long COVID be considered an occupational disease?
The consequences of a Corona virus SARS-CoV-2 infection can be recognised as an occupational disease or accident at work provided the infection was in the occupational context and certain conditions are fulfilled. This also includes Long COVID symptoms, which occur if you initially had no signs of illness immediately after infection with the corona virus. If symptoms that are to be regarded as a result of the infection only occur later, an occupational disease can be recognised from this point in time.
In such cases, statutory accident insurance is responsible. The affected persons are then entitled to benefits from statutory accident insurance, such as medical treatment, medical rehabilitation and benefits for occupational participation. After notification, the relevant accident insurer checks whether recognition is possible.
Recognising COVID-19 and therefore also Long COVID as an occupational disease is generally only possible for certain occupational groups. This includes employees in the health service, in welfare work or in a laboratory, who are at particularly high risk of infection in the workplace. However, under certain circumstances, it may also be possible to recognise people who have a similarly high risk of infection in their profession. After notification, the relevant accident insurer checks whether recognition is possible.
Infection with the corona virus must also lead to symptoms in order for an occupational disease to be recognised. This also includes Long COVID symptoms, even if you initially had no signs of illness immediately after infection with the corona virus. If symptoms that are to be regarded as a result of the infection only occur later, an occupational disease can be recognised from this point in time.
Detailed information on this topic can be found at the German Social Accident Insurance. You will receive a general overview of the topic of occupational disease in a video. Employees in healthcare professions can obtain further information, from among other places, at the Trade association for health service and public welfare work (BGW).
When can Long COVID be considered an occupational accident?
A job-related infection and subsequent COVID-19 illness and its possible long-term effects can be considered as accident at work if the prerequisites for the recognition as occupational disease are not fulfilled.
Infection with the corona virus must occur in the event of an occupational accident as a result of an activity that is covered by statutory accident insurance. In addition to employment, this can also include, for example, attending school or university, taking on certain voluntary posts or providing first aid. An accident at work can also occur if you catch an infection on the way to such an activity or on the way back. As a rule, intensive contact with at least one infectious person must be proven. The Robert Koch Institute (RKI) explains on its web page when there is an increased risk of infection in the event of contact. In contrast, infection in the uninsured private sphere must not be sufficiently probable.
The information page of the Statutory Accident Insurance (DGUV) offers detailed information on when the effects of a Corona virus infection can be an occupational disease or an accident at work.
What should you do if you suspect an occupational disease or an occupational accident?
The required proof of an infection by the SARS-CoV-2 virus had to be strictly provided by a positive PCR test until now; this continues to be eligible as a proof of an infection. But the proof of an infection can also be provided by a positively qualified rapid antigen test (POC rapid test). The rapid antigen test is qualified if it has been conducted by medical professionals. Whereas, a self-test by the patient – even if he/she is medically trained – is not enough for a proof of infection. The German Social Accident Insurance provides information on its web page. Doctors and employers are obliged to report suspected occupational diseases to the statutory accident insurance. Notification may also be mandatory in the event of an accident at work. Affected persons themselves can also contact their accident insurer at any time in case of suspicion of an infection caused at work.
The affected persons can also report such suspicions themselves. An informal notification to the competent statutory accident insurance is sufficient. Before reporting, you can seek advice from a doctor, for example from the company medical service. The possible connection between the activity and the complaints should be pointed out here.
Which accident insurer is responsible?
In Germany, statutory accident insurance is divided into three areas:
- Employer's liability insurance associations: Private companies and their employees are insured here.
- Public sector accident insurers: State-owned companies, companies of the federal states and municipalities and their employees are insured here.
- Agricultural accident insurance: It insures companies in agriculture, forestry and horticulture and their employees. Further information can be found on the website of the Social Insurance for Agriculture, Forestry and Horticulture (SVLFG).
If you are unsure which insurance provider is responsible for you, you can contact the information hotline of the statutory accident insurance. You can reach them Monday to Friday from 8 a.m. to 6 p.m. free of charge on 0800 6050404.
Last update: July 2024
Who shall bear the costs arising due to Long COVID?
A large number of cost bearers are involved in the care of people suffering from Long COVID:
- statutory health insurance (GKV)
- private health insurance (PKV)
- statutory pension insurance
- statutory accident insurance
- nursing care insurance
Treatment costs
The statutory and private health insurances bear the costs for their policy holders when treatments are required.
Transitional payment
Transitional payment is a so-called wage replacement benefit. You can apply for this money if there is no longer a claim to continuation of payment due to a case of illness. Long haulers can receive transitional payment, for example, under certain conditions of a medical or occupational rehab measures or during a reintegration at work. Long haulers must either be paid pension contributions before the start of benefits or have drawn certain other benefits beforehand. Such benefits include, for example, sickness benefit, unemployment benefit, and maternity benefit. However, pension contributions must have been paid even before these benefits.
People who have claim to unemployment benefit can also receive transitional payment in certain cases. It relates to people, who are participating in rehab measures and therefore cannot work full day.
If long haulers get sickness benefit under § 44 of SGB V and need only a few payments for prevention or follow-up, the long haulers can also receive transitional payment under certain conditions.
You can find further information in the brochure of the German Pension Insurance.
Reintegration at work
The pension insurance bears the costs for reintegration at work and payments for participation for COVID long haulers.
You can find further information in the brochure of the German Pension Insurance.
Reduced earning capacity pension
In certain cases, a reduced earning capacity pension of the statutory pension insurance can be worth considering in certain cases for COVID long haulers. The reduction in earning capacity is divided into 2 sages: People are fully disabled if they can be gainfully employed in the general job market for less than 3 hours a day. Partially disable people are those whose remaining performance capacity is at least 3 and less than 6 hours a day. If the insured people were born before 2 January 1961, they can receive a half reduced earning capacity pension in case of inability to work.
You can find further information on the website of the German Pension Insurance.
Benefits upon needing care
COVID long haulers possibly need help in everyday life. If you can no longer manage certain things on your own, you potentially have a claim to benefits of nursing care insurance. The benefits depend on how much in need of help you are. That is decided by an assessment by a Medical Service or other independent reviewers. Your illness is not decisive here. Rather, it is considered how greatly long haulers are affected and thus restricted in everyday life. The need for care must persist for 6 months at least and have a certain severity. The care insurance finally decides on the level of care and taking into account the expert opinion.
Read more about the benefits of care insurance on the website of the Federal Ministry of Health.
Benefits in an occupational disease or an accident at work.
In some cases, a Long COVID illness can be recognised as a consequence of an occupational disease or accident at work by the statutory accident insurance. Following a recognition, the competent accident insurer takes over the required payments. Such payments include, for example, the medical treatment and rehab measures as well as benefit in lieu of income, if you are temporarily incapable of work. If you have permanently limited earning capacity on the general job market after an insured event, an insured person’s pension comes into question. Payments for reintegration at work and social reintegration as well as care and in case of death, survivor’s benefits can be borne by the accident insurance. The responsible body of the statutory accident insurance determines ex officio, whether such payments come into question.
Therefore, you generally do not have to apply for the payments.
Also read the question “Long COVID be an occupations disease or an accident at work?”.
Sources:
https://www.dguv.de/de/reha_leistung/index.jsp
Further information:
https://www.test.de/Long-Covid-Ploetzlich-ausgebremst-5933790-5933796/
Last update: July 2024
When is company integration management (BEM) carried out?
Some people are unable to work due to Long COVID and need support to get back to work. If an employee is unfit for work for a total of more than 6 weeks within a 12-month period, the employer must generally offer a company integration management (BEM). All employers are obliged to do so, regardless of the size of the company or the field in which they operate. The HR department or the company medical service can provide support in planning the BEM measures if necessary. The employer can also involve the rehabilitation organisations in the BEM procedure. These can provide information on suitable rehabilitation services, for example. Participation in the BEM is voluntary for employees.
Information and counselling on the BEM is provided by the Deutsche Rentenversicherung und die Bundesarbeitsgemeinschaft für Rehabilitation e. V. (BAR). You can also find more information on help with returning to work in the FAQ “What is gradual reintegration and how does it work?”.
Last update: July 2024
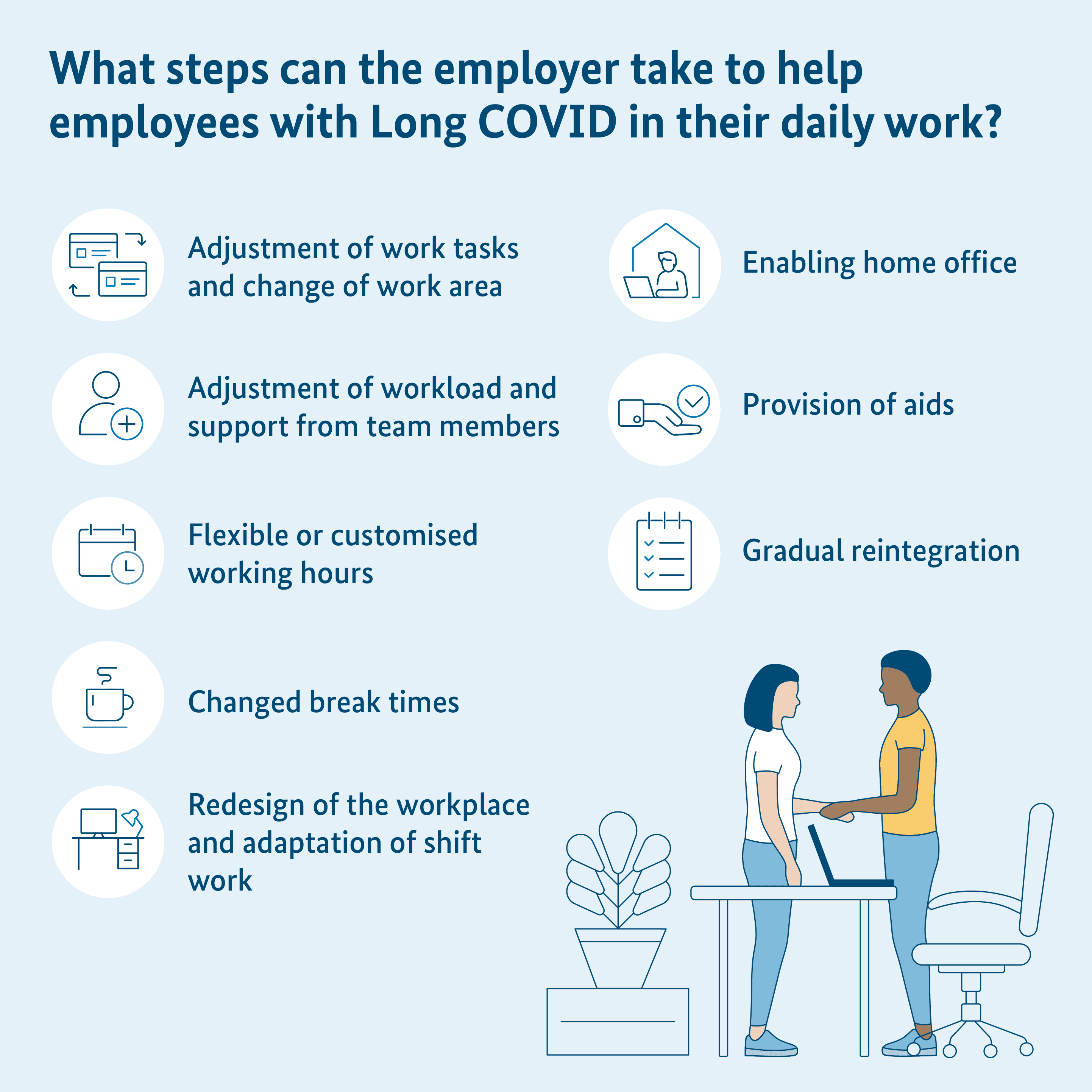
What support can people with Long COVID get in the workplace?
Support should be tailored to the needs of the affected person. Measures should therefore always be jointly agreed, regularly reviewed and adjusted if necessary. The European Agency for Safety and Health at Work has developed a Guide for managers for dealing with Long COVID. There you will find, among other things, information on planning your return to work and possible options of support. Another Guide for employees during recovery is aimed at people who have a job, are looking for a job or are starting a new job. Both guides are available in German and many other languages.
The Confederation of German Employers' Associations (BDA) also provides Information on Long COVID especially for employers.
There are various ways in which sick employees can be supported in the work environment:
- Adaptation of tasks
- Change of work place
- Workload adjustment
- Support by other team members
- Adjustment of working hours
- Flexible working hours
- Changes to break times
- Shift work adjustment
- Design of the workplace
- Enabling home office
- Providing aids
- Adaptation of the workplace
- Gradual reintegration
- Approval of reintegration plan
- Support for implementation
Last updated: July 2024
What is gradual reintegration and how does it work?
After a longer period of sick leave, gradual reintegration can make it easier to return to your previous job. A personalised plan with individual stages is drawn up for this purpose. The requirements are gradually increased with each stage. The aim is to be able to work full-time in your previous job again at the end of the reintegration programme. As a rule, reintegration should not exceed a period of 6 months. However, it may be necessary for persons affected by Long COVID to return to work more slowly and carefully than usual. Other measures in the workplace can also support the return to work.
Who can do a reintegration?
Certain conditions need to be met for reintegration:
- You would like to return to your previous job after an illness.
- You are still on sick leave.
- From a medical point of view, you are resilient enough for a gradual return to work.
- Doctors, the employee and the employer agree to the reintegration.
Sickness benefit or transitional allowance?
You continue to be considered as incapable of work (“on sick leave”) during the reintegration. Therefore, benefits in lieu of income such as sickness benefit of the statutory health insurance or the compensation for injury of the statutory accident insurance generally continue to be paid. If the gradual reintegration takes place following medical rehabilitation, transitional allowance can also be paid during the gradual reintegration.
What is a stress test?
A stress test can determine whether a gradual return to work is possible. This can happen at the end of medical rehabilitation, for example. If you are not yet resilient enough, occupational therapy may be an option. This involves, for example, training specific activities from professional life. Occupational rehabilitation measures can help to increase resilience. A stress test can be repeated regularly.
How does the application and reintegration process work?
The following steps are usually necessary:
- Counselling: You should seek counselling on the subject of reintegration. A good point of contact is the doctor treating you, for example your family doctor. The company medical service can also help. If you are undergoing rehabilitation, counselling can take place there or you can contact the relevant rehabilitation provider directly.
- Reintegration plan: A personal reintegration plan is drawn up together with a doctor. You can also specify which tasks and how many working hours are possible each day. The employer must also agree to the plan. In some cases, the company doctor responsible must also approve the gradual reintegration.
- Application: Once everyone has agreed to the plan, reintegration must be applied for. The application is submitted to the health insurance company or the pension insurance, depending on which is responsible. If Long COVID has been recognised as an occupational disease or occupational accident, the statutory accident insurance is the right point of contact.
- Also: The progress of reintegration is regularly reviewed at medical appointments. If necessary, you can adapt the plan as you go along. It is also possible to cancel the plan. Sometimes a gradual reintegration programme is ended earlier because the person concerned is already fully fit for work again.
Die Bundesarbeitsgemeinschaft für Rehabilitation e. V. (BAR) in its brochure “Gradual reintegration into the work process” provides detailed information and case studies.
Sources:
https://www.bar-frankfurt.de/service/publikationen/produktdetails/produkt/173.html
https://www.g-ba.de/downloads/62-492-2922/AU-RL_2022-08-04_iK-2022-08-04.pdf
https://www.einfach-teilhaben.de/DE/AS/Ratgeber/02_Hamburger_Modell/Hamburger_Modell_node.html
https://www.bih.de/integrationsaemter/medien-und-publikationen/fachlexikon-a-z/belastungserprobung/
Last updated: July 2024
How is a severe disability determined?
Severe disability status is not recognised on the basis of a specific disease or diagnosis (e.g. cardiovascular disease, Long COVID or Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (ME/CFS)). The nature and severity of the respective impairment alone are the decisive criteria.
The Ordinance on Medical Care for Victims (VersMedV) contains the principles for assessments according to the law on severely disabled persons. ME/CFS is taken into account here. Where ME/CFS impairs participation, this may lead to the determination of a degree of disability (GdB).
According to the Ordinance, the degree of disability for ME/CFS can vary between 0 and 100 depending on the severity of impairment it causes in the individual case at hand. This provision takes into account the fact that ME/CFS is characterised by a wide range of symptoms. In addition to the fatigue of unknown cause for at least six months, the affected persons complain of a variety of other symptoms, which may be more or less pronounced depending on the individual case and can occur in very different combinations. The symptoms often come and go over time, with alternating periods of relapse and improvement. Moreover, this trajectory can also vary widely from case to case, with correspondingly different impacts on participation. The assessment criteria allow for the fact that the disease can impact each individual differently when it comes to participation.
An application for the determination of a severe disability must be submitted to the relevant social affairs office (Versorgungsamt). This office can be found here.
Letzte Aktualisierung: October 2025
Useful links
Rehabilitation und Rückkehr in den AlltaRehabilitation and return to everyday life
- Information supply regarding rehabilitation services of the Federal Ministry of Labour and Social Affairs (BMAS)
- Rehabilitation facility register of the Federal Association for Rehabilitation (BAR)
- Information about Long COVID rehabilitation from Deutsche Rentenversicherung
- Information about operational integration management at einfach-teilhaben.de
- Information about operational integration management from the Federal Association for Rehabilitation (BAR)
Long COVID in studies and the profession
